This summarizes a selection of applications for the Experimental Radio Service received by the FCC during April and May 2011. These are related to TV white space, electromagnetic compatibility testing, train control, point-to-multipoint communications, satellite communications, radar, unmanned aerial vehicles, GPS, ultra-wideband, mobile satellite service, UMTS, mobile broadband picocells, wireless backhaul, and IEEE 802.11p. The descriptions are sorted by frequency.
Elite Electronic Engineering filed an application for special temporary authority to conduct radiated radio-frequency susceptibility testing on a cotton harvesting machine. The testing is intended to determine the ability of the vehicle to operate safely in its electromagnetic environment without any change in state, function, or performance. Testing is to take place near Kimballton, Iowa on various frequencies in the 20 MHz – 2.5 GHz range. The tests are to be done outdoors because a sufficiently-large indoor shielded test chamber could not be found. Sirius XM Radio objects to the proposed tests out of concern for potential harmful interference to its operations.
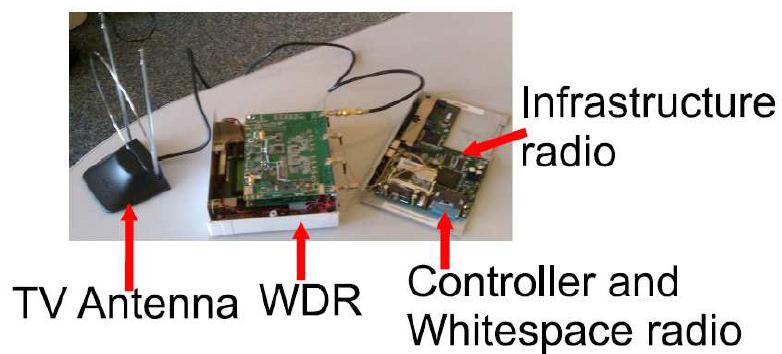
Alcatel-Lucent filed an application and exhibits for experimental license to study white-space communications implemented using existing air interfaces such as LTE along with cognitive radio sensing and dynamic spectrum management overlays. The fixed and mobile equipment will utilize a software-defined wideband digital radio (WDR) from Rutgers WINLAB. Operation will be on various TV channels in the 174-698 MHz band around Murray Hill, New Jersey.
Carlson Wireless filed several applications for temporary TV white space operation, including in Cordova, Alaska to test the use of TV white space in supporting remote telephony connections. Operation will be in TV bands 174-216 MHz and 470-680 MHz.
Niitek, Inc. filed an application and exhibits for special temporary authority to test ground penetrating radar (GPR) in Dulles and Charlottesville, Virginia on 200-7,000 MHz. The radar uses ultra-wideband (UWB) technology. The GPR is for use in a landmine detection system that has been procured by the U.S. Army for use in the Middle East. A variety of shielding and power control measures will be used to reduce the potential for interference to other radio services.
Lilee Systems filed an application and exhibits for experimental license to test a positive train control system consisting of three components: locomotive radio, wayside radio, and base-station radio. The company is developing a product family supporting the positive train control effort mandated by the Federal Railroad Administration. Operation will be in New York, New York on 217-222 MHz.
Chevron USA filed an application and exhibit for special temporary authority to test an experimental fixed-link communications system connecting offshore platforms in the Gulf of Mexico. In 2008, Chevron participated in FCC Auction No. 73 and was the high bidder for the 700 MHz band A (698-704/728-734MHz), B (704-710/734-740MHz), and E (722-728MHz) blocks covering the Gulf of Mexico. The tests will be on 703.55-704.45 MHz and 733.55-734.45 MHz. The equipment that Chevron proposes to test has been certified internationally, but not for the lower 700 MHz band in the United States. If the tests are successful, the equipment manufacturer will seek certification from the FCC. Chevron plans to use this equipment to enhance the capabilities of its point-to-multipoint WiMAX network and provide high-speed network connections to existing and future production platforms.
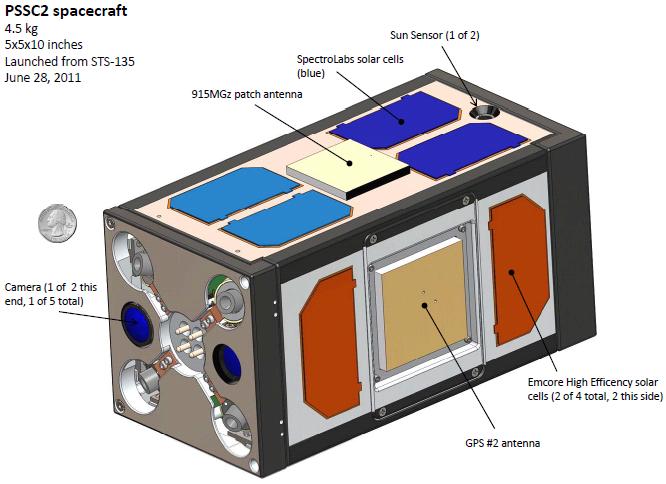
The Aerospace Corporation filed an application and exhibits for special temporary authority to operate a satellite link in support of research into the space application of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) components and related microelectronics technologies. The test includes a demonstration of principles of the physics of the low-earth-orbit space environment and its effects on MEMS microelectronics. The satellite weighs 11 pounds and its dimensions are 5x5x10 inches. It’s to be deployed during the last space shuttle mission, STS-135, which is now scheduled to launch July 12. The satellite has two radios for redundancy, both operating on 914.7 MHz, and both using an omni-directional patch antenna.
The Maryland Department of the Environment filed an application and exhibits for experimental license to use wind-profiling radar to study the transport of air pollutants such as ground-level ozone. The radar is a boundary-layer profiler, and depends on the scattering of a transmitted signal by irregularities in the index of refraction of the air caused by turbulent eddies in the wind. By receiving the scattered signal and determining the Doppler frequency, the speed of the wind can be determined. The radar consists of a vertically-looking antenna subsystem, a transmitter subsystem capable of unmodulated and phase-modulated pulses, a receiver subsystem, a signal processing subsystem performing target parameter extraction and identification, and a data processing/communication subsystem for charting, recording, and transmitting results. Operation will be on 915 MHz at Cambridge, Maryland.
BAE Systems filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to operate on 1370-1390 MHz in Tucson, Arizona to test a new radio modem, transmitter, and receiver on the Silver Fox unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) as part of a U.S. military project.
LightSquared filed an application and exhibits for special temporary authority to conduct testing to determine the effects of L-band LTE signals on GPS devices in a live field-test environment. The testing is an outgrowth of the requirements established in FCC Order DA 11-133 granting LightSquared, a Mobile Satellite Service (MSS) licensee in the L-Band, a conditional waiver of the Ancillary Terrestrial Component (ATC) “integrated service” rule. The requested frequency bands include 1526-1536 MHz and 1545.2-1555.2 MHz.
Qualcomm filed an application and exhibits for experimental license to test time-division duplex (TDD) technology in San Diego, California and Bridgewater, New Jersey. Operation will be on 1,915-1,920 MHz. A single fixed transmitter will be installed and operated at each location. Mobile units will operate within a 5 mile radius of the fixed sites.
Western DataCom filed an application and exhibit for special temporary authority to test the range and throughput of a UMTS cellular-based system mounted to an aerostat. Operation will be at South Boston, Virginia on 1972.5 MHz and 2162.5 MHz, with the antenna about 800 meters above ground.
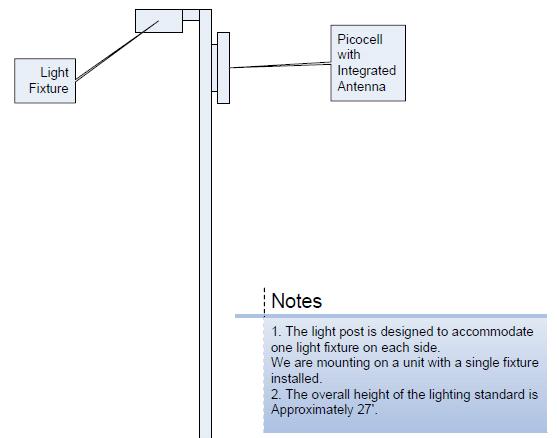
Powerwave Technologies filed an application and exhibits for experimental license to operate a small network to test LTE picocell technology, including aspects related to handover, QoS, power control, and resource scheduling. The test will take place in Santa Ana, California on 1,710-1,755 MHz and 2,110-2,155 MHz.
ETS Technologies filed an application and exhibits for experimental license to test non-line-of-sight wireless backhaul technology for 4G systems. Operation will be in San Jose, California on 3,700-4,200 MHz.
Qualcomm filed an application and exhibit for experimental license to test IEEE 802.11p Dedicated Short Range Communications (DRSC) mobile devices in Bridgewater, New Jersey and New York, New York. Operation will be on 5,850-5,925 MHz. DRSC is a short-range communications service for roadside-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-vehicle links that are part of the Intelligent Transportation System (ITS). Compared to 3G or 4G mobile broadband, DSRC acts as a complement with higher data rates and lower latency over a small area. In addition to the DRSC tests, Qualcomm will evaluate new proprietary OFDM technology operating within the same DRSC channel bandwidths.
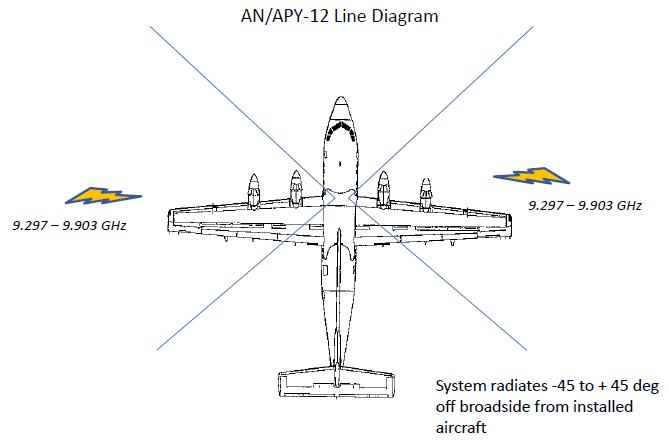
Lockheed Martin filed an application and exhibits for special temporary authority to test enhancements to an existing AN/APY-12 modular Ground Moving Target Indication (GMTI)/Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR). The enhancements are brought about by changes in operational requirements by the U.S. Army in Korea. This testing is required prior to integration and deployment of the radar system in an Airborne Reconnaissance Low (ARL) aircraft. The testing will involve detection and analysis of moving and fixed targets in open and urban settings. Testing will be on 9.297-9.903 GHz in Goodyear, Arizona and Hagerstown, Maryland.
Raytheon filed an application and exhibit for special temporary authority to conduct ground and airborne test and evaluation of design modifications and mode implementations to the APY-10 Radar. This product is for a direct commercial sale between Raytheon and Boeing, for a user in India. The modifications, required in part due to export restructions, reduce the accuracy of the radar by removing accumulated carrier phase measurement, removing 1 and 3 foot-resolution synthetic aperture radar (SAR) capability, and limiting performance to meet 30 meter SAR geo-location accuracy. Operation will be within 200 miles of Sherman, Texas on 9.350-10.150 GHz.
Niitek, Inc. filed an application and exhibits for special temporary authority to test a ground radio link intended to enhance the capability of the company’s landmine detection system. The system has been procured by the U.S. Army for use in Afghanistan. The enhancements provide data communication between a primary landmine detection vehicle and a second route-clearance vehicle. Operation will be on 14.7145-15.1365 MHz and on 15.1900 MHz.