This summarizes a selection from 173 applications for the Experimental Radio Service received by the FCC during August and September 2011. These are related to long-range low-frequency radar, amateur radio, shortwave data, wireless microphones, single-sideband, mine detection, millimeter-wave communications, signal intelligence, automotive radar, satellite feeder links, meteor-burst communications, aircraft telemetry, white space systems, border security radar, 3G and 4G applications, RFID, wind turbine testing, unmanned aerial vehicles, spacecraft telemetry and control, aircraft passenger broadband, and autonomous aircraft landing systems. The descriptions are sorted by the lowest frequency found in the application.
- Amateur Radio operator Juan Granados filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to test CW, LSB, RTTY, and digital modes such as BPSK on 130-140 kHz and 495-505 kHz. The testing will take place in Miami, Florida and involve communication with amateurs in other parts of the world.
- Cognitive Data Dispatch (CDD) filed an application with exhibits for experimental license to “explore the possibility of a cognitive type of radio architecture in transmitting very brief time duration data transmissions over a HF radio channel.” “CDD is seeking authority to transmit data in a point-to-point mode using a minimal spectral footprint (utilizing a channel for less than 10 milliseconds at a time, not to exceed 250 milliseconds of total occupation during any 24 hour period) on pre-coordinated HF frequencies using fixed transmit and receive locations. These extremely brief time duty duration transmissions will ensure no harmful interference will occur to any licensed users of these channels. As part of the channel selection process, CDD transmissions will employ cognitive radio features to ensure the optimum transmission channel and minimal opportunity for interference.” Operation will be from sites in Aurora, Illinois; Washington, DC; and East Rutherford, New Jersey on various frequencies from 2.2890 MHz to 7.6971 MHz.
- RIIMIC LLC, d.b.a. Sunair Electronics filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to conduct testing of single-sideband communications equipment in Ft. Lauderdale, Florida on 5.888-23.1465 MHz.
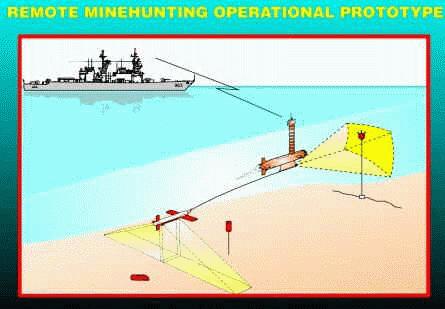
- Lockheed Martin filed an application with exhibit for experimental license for control operation of the AN/WLD-1(V) Remote Multi-Mission Vehicle (RMMV) in support of the US Navy’s Remote Minehunting System (RMS) and Multi-Vehicle Communication System (MVCS) programs. This experiment is said to be necessary for development and integration of the radio communication link between the control and remote stations. Operation will be in West Palm Beach, Florida on various frequencies between 30-40 MHz and 1708-2297 MHz.
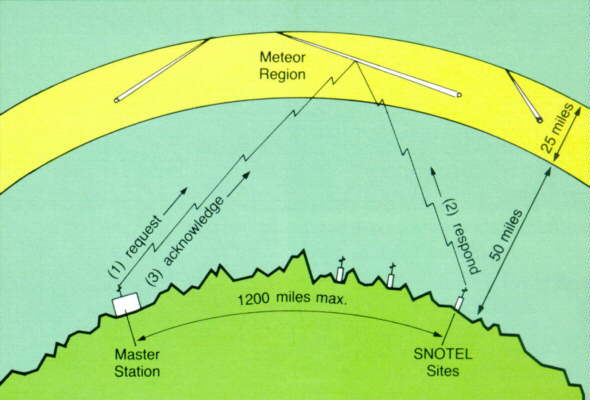
- Signal Systems Corporation filed an application with exhibits (several confidential) for special temporary authority to test the utility of short duration messaging in the VHF band using meteor burst communications). Data rates will be up to 9600 bps. Operation will be in Ridgley, Maryland and Blacksburg, South Carolina on 40.75 and 49.8 MHz.
- Live2Media filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to test “media broadcast” at an auto race event. The broadcast will consist of messages from the pit crew to the race car, along with announcements. Operation will take place in Laguna Seca, California on several frequencies between 64.0 MHz and 68.2 MHz.
- Garmin filed an application with exhibits for experimental license to test the interoperability of its avionic data link system and data link radio (GDR 66) with an ARINC ground station. The link is characterized by 8-DPSK modulation, 25 kHz channel spacing, a raw data rate of 31.5 kbps, and a carrier-sense multiple-access technique for operation on a shared channel. Operation will be in Olathe, Kansas on 136.975 MHz.
- Adaptrum filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to experiment with prototype TV white-space equipment. The equipment is to be fully compliant with the new white space rules except for equipment authorization. Operation will be in San Jose and Mountain View, California on 174-216 MHz, 470-608 MHz, and 614-698 MHz.
- The Rappahannock Electric Cooperative (REC) filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to test the usefulness of TV white-space frequencies in, as the applicant states, “supporting smart grid fixed and mobile data connectivity. Fixed applications include long range point to multipoint backhaul of internal utility traffic including supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) traffic and automatic metering infrastructure (AMI) traffic, both located at REC’s electric utility substations. The AMI system also enables real-time load management thereby improving system reliability and reducing peak demand, all of which further the nation’s goal for greater energy independence and reduced carbon emissions. In terms of mobile data connectivity, REC plans to leverage this technology to test the efficacy of these frequencies for mobile workforce management applications in the utility service vehicles including processing work orders – new connects, disconnects, reconnects, and outage orders. REC also has a need to test automatic vehicle location (AVL) to optimize routing of service vehicles in real time.” Operation will be in several Virginia communities on 174-216 MHz.
- The Avionics Engineering Center at Ohio University filed an application with exhibits for experimental license to operate in support of research on the Joint Precision Approach and Landing System (JPALS). The system is intended to provide fixed and mobile precision approach and landing systems that will support a 200 feet decision height and 0.5 statute mile visibility while operating in military or civil modes. The system will also support auto-land capability for suitably equipped aircraft (to include Army, Navy, Marine Corps, and Air Force aircraft) and operate in a GPS-jamming-threat environment. Operation will be in Albany, Ohio on 240.650 MHz and 280.975 MHz.
- Lockheed Martin filed an application with exhibits for experimental license to “perform testing on a Low Frequency Sensor (LFS) radar that will be used for long range detection. The testing will evaluate the sensor detection performance and antenna characterization of the radar.” The test antenna will be log periodic with a gain of 6 dBi and beamwidth of 103 degrees. ERP will be variable up to 10 watts. Operation will be in Syracuse, New York on 420-450 MHz.
- KTS Wireless filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to test a TV white-space system in an orange grove located southwest of Clewiston, Florida. The intent is to apply TV white spaces to the problem of enabling automation for sustainable specialty crop farming. “The current implementation requires a multi-radio solution in several bands with multiple repeaters which is problematic in an industrial environment.” The white-space method is intended to allow a single base-station solution. Operation will be on 470-608 MHz and 614-698 MHz.
- Google filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to operate in support of experiments in TV white spaces in the bands 512-602 MHz and 620-698 MHz. “Google will conduct research and experiments of fixed and personal/portable devices within the white spaces to determine the potential utility and feasibility of such operations and technology. Google requests authorization within the geographic coordinates of its Mountain View, California campus. Google plans to operate up to three fixed base stations at 4 W per 6 MHz channel available, with a radius of operation of 5 miles (8.05 km), and up to 50 mobile stations at 100 mW per 6 MHz channel available.”
- Quantum5x Systems filed an application for special temporary authority to test a “new type of wireless microphone with a rubberized housing and internal antenna, as well as addressing de-sense and intermodulation correction technology.” Operation will in New York, New York on 600-608 MHz and 614-689 MHz.
- Lockheed Martin filed an application with exhibits for special temporary authority to test its “MONAX Cellular solution along the southwest border of Texas. This operation will be supporting evaluation by local and state authorities of the MONAX solution for utilization in securing the border with Mexico.” “MONAX is a powerful, new communications system that combines the convenience of smartphone technology with the power and flexibility of a secure, highly portable infrastructure.” “The 4G wireless system, consists of a unique portable MONAX Lynx sleeve that connects touch-screen COTS [commercial off-the-shelf] smartphones [which look similar to iPhones] to the MONAX XG Base Station infrastructure on the ground or in airborne platforms, offering uninterrupted service to warfighters in the field.” “MONAX offers a rich set of applications and governance, leveraging commercial smartphone application development and application store model. Applications can be easily written or re-hosted on a smartphone, reviewed/approved for mission effectiveness, hosted in a 24×7 app store and made available to the warfighter.” Operation will be near Finlay, Texas on 758-763 MHz and 788-793 MHz.
- Vodafone filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to “test and demonstrate advanced Internet services in . . . GSM, HSPA and LTE environments, such as GPRS (general packet radio system), location-based services, transcoding between email, SMS, and WAP, and secure position/mobile-commerce services.” Operation will be in Redwood City, California on 842-850 MHz, 890-893 MHz, 935-938 MHz, 1920-1936 MHz, 2110-2126 MHz, 2500-2520 MHz, and 2620-2640 MHz.
- Western DataCom filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to test UMTS wireless devices used by the Intelligence & Information Warfare Directorate of the US Army Communications Electronics Research, Development, and Engineering Center. The system is to be used for transmission and reception of voice and data within a single network; it does not connect to any other provider’s network. Operation will at Fort Dix and Lakehurst, New Jersey, on 900-915 MHz, 945-960 MHz, 1755 MHz, 1850 MHz, 1972.4-1977.4 MHz, and 2162.4-2167.4 MHz.
- General Dynamics filed an application with exhibits for experimental license to conduct testing in support of its Labrador program, which is intended to develop methods for locating and identifying radio frequency signals using a variety of devices. The project requires communication between collaborating software-defined radios. Operation will be in Ypsilanti, Michigan; Bloomington, Minnesota; Tucson, Arizona; and Austin, Texas on 902-928 MHz, 1350-1390 MHz, and 1755-1850 MHz.
- Wal-Mart Stores filed an application with exhibits for experimental license to conduct RFID research at its lab in Fayetteville, Arkansas. This research relates, in part, to optimal placement of RFID tags on cases, pallets and assets. “The experimentation will include RFID tagged cases going through a simulated supply chain. This will include testing in a dense reader mode environment. Additional testing will be conducted using RFID enabled handhelds for inventory collection, product locating and product receiving in a simulated store environment. RFID readers fixed to mobile assets (forklifts, carts, wearable devices) will be tested using this site license to ensure that solutions developed using RFID readers in the United States will meet the given performance criteria across all other regions worldwide within which Wal-Mart operates.” Operation will be on 902-928 MHz.
- General Electric Global Research filed an application with exhibits for special temporary authority to test a microwave imaging system for non-destructive testing of in-service wind turbine blades. Operation will take place in Schenectady, New York. The signal will be a broadband linear chirp swept from 1 GHz to 18 GHz up to 10 times per second.
- Rockwell Collins filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to develop and test equipment used in the Aeronautical Mobile Satellite Service. Four Inmarsat geostationary satellites will be used. Operation will be nationwide on 1626.5-1660.5 MHz.
- BAE Systems filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to conduct proof-of-concept tests for the next generation of communication-intelligence unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Operation will take place in Hudson, New Hampshire on 1760-1840 MHz, 2365-2445 MHz, and 10.25 GHz.
- Ericsson filed an application and exhibit for experimental license to conduct tests related to 3G and LTE application performance. “This investigation will examine a new aspect of network performance and will contribute to expansion of the mobile ecosystem. Historically, the wireless industry has relied solely on bandwidth or transmission rates to assess performance. However, the expanding variety of applications that will run over networks indicates that network performance should also be investigated through the lens of application performance. The uniqueness of the planned experiment is to understand the performance of new, varied applications and services on mobile networks.” Operation will take place in San Jose, California on 1920-1930 MHz, 2110-2120 MHz, 2500-2520 MHz, and 2620-2640 MHz.
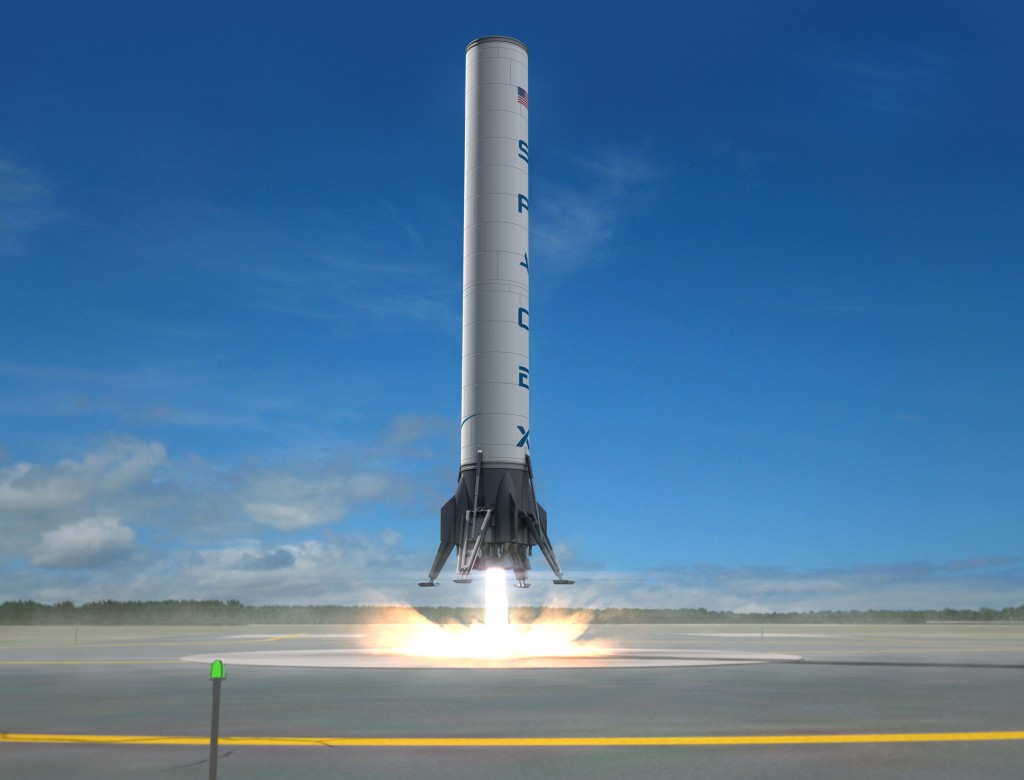
- Space Exploration Technologies filed an application with exhibits for experimental license to operate in support of R&D for a Vertical Takeoff, Vertical Landing (VTVL) vehicle on its test site in McGregor, Texas. The vehicle is to take off, ascend vertically to a low altitude, and then descend back to its original landing spot. “The tests themselves are divided into low?altitude and higher?altitude tests. The low?altitude tests stay below 215 meters in altitude and last approximately 45 seconds. These tests will be run approximately three times per week during the initial portion of the program. The higher?altitude tests can go as high as 3.5 km and will occur approximately once per week. These tests last approximately 3 minutes.” A downlink is used so operating parameters can be viewed in real time. An uplink is used in case of an anomaly, so the vehicle can be commanded into a safe state. Operation will be on 2040.5675 MHz, 2221.5 MHz, and 2273.5 MHz.
- Space Exploration Technologies filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority for “telemetry and video transmissions during launch (and pre-launch checks) for an orbital test flight of the Falcon 9 launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral, pursuant to the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) Demonstrations agreement with NASA. The launch date is currently scheduled for November 30, 2011.” “The purpose of the operation (the Demo C2/3 mission) is to demonstrate the capability to launch a capsule that can dock with the International Space Station.” “[S]pectrum support for the capsule is already being handled by NTIA (via NASA). Accordingly, STA will only cover the launch vehicle stages (first stage and second stage), during launch, as well as pre-launch checks.” Operation will be on 2213.5 MHz, 2221.5 MHz, 2251.5 MHz, 2273.5 MHz, and 5765 MHz at Cape Canaveral, Florida.
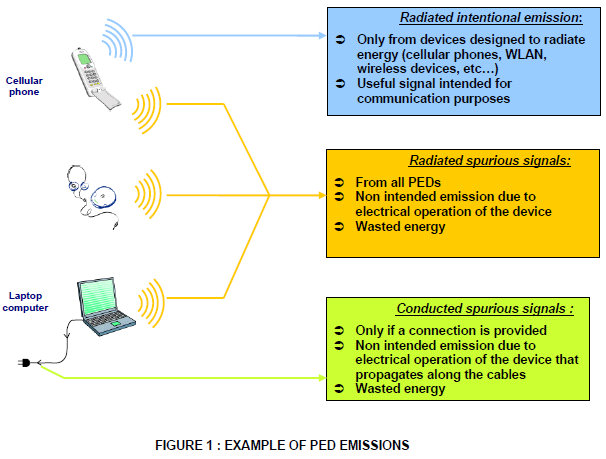
- Panasonic Avionics Corporation filed an application with exhibits for special temporary authority to conduct ground testing of potential interference from portable electronic devices (PEDs) in aircraft. This is in support of Panasonic’s Global Communications Suite (“GCS”) featuring the “eXConnect” Ku-band aeronautical mobile-satellite service system providing broadband connectivity on the aircraft during flight. Testing will be in Everett, Washington on 2386-2505 MHz, 5150-5350 MHz, and 5715-5835 MHz.
- Gibbons Systems Inc. (GSI) filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to test a new air-to-air ranging system as part of a contract with Wright-Patterson Air Force Base. The applicant is developing the system to “fundamentally improve radio ranging among the C-130 fleet deployed by the United States Air Force. Currently, the C-130 fleet utilizes high powered radio transmissions, similar to radar, for maintaining formation, which nonetheless render the formation highly detectable and, thus, vulnerable to enemy monitoring. The GSI RF technology employs several techniques (including low duty cycle, low total signal energy, and high bandwidth) to render the signals difficult to detect, i.e. ‘low probability of detection’ (‘LPD’). “Operation will be in Redwood City, California on 2500 MHz.
- Aurora Flight Sciences filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to operate in support of the development of an Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS). The applicant says existing data-link systems don’t provide the necessary data rate of 10 Mbps. An auto-tracking antenna, designed for use with this system, combines a high gain directional dish, a low-gain omni-directional antenna, and associated auto-tracking hardware. The omni-directional antenna is for close-in operation of the aircraft, such as during takeoff and landing, where the angular velocity of the aircraft relative to the antenna is too great to track. The high-gain antenna is for long-range operation. “The auto-tracking antenna is provided with the GPS position of the aircraft. Tracking is accomplished using a combination of GPS and signal strength. Signal strength is used to find the aircraft when the tracking is not locked, and GPS is used to follow it thereafter.” Operation will be in Warrenton, Virginia on 4.4-4.8 GHz.
- Motorola Solutions filed an application with exhibits for experimental license to test the outdoor link performance of its RDB350 point-to-multipoint data transceiver. The intent is to test fixed and mobile outdoor data transmission for federal users. The system is based on the IEEE 802.16e standard. Operation will be in Schaumberg, Illinois on 4600-4800 MHz.
- Raytheon Network Centric Systems filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to test a mobile surveillance system based on commercial off-the-shelf radar, electro-optical/ Infrared cameras, and microwave communications (i.e., the Motorola PTP 48600 wireless Ethernet bridge). The system is intended to “monitor international borders.” Operation will be near Las Cruces, New Mexico on 4720-4990 MHz. A similar application was filed for operation near McKinney, Texas.
- Miltec Corporation filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to conduct tests, as part of a U.S. Army contract, in support of the Innovative Waterside Wide-Area Tactical Coverage and Homing Sensors (IWWS) program intended to detect, track, and classify people and vessels in a maritime environment above and below the surface of the water. Operation will be in Kingsport, Tennessee and Guntersville, Alabama on 9.38-9.44 GHz.
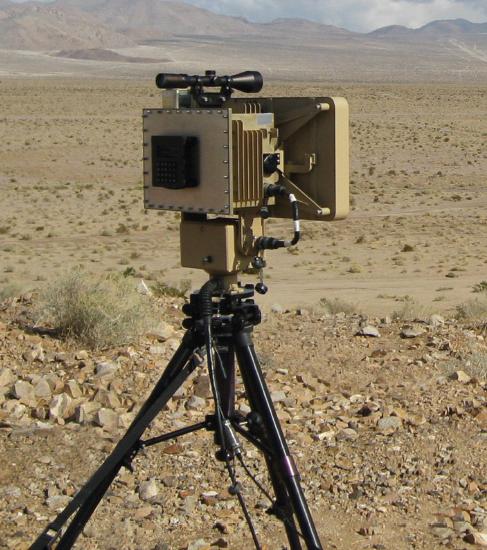
- SAIC filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to test“low-power land radar” on 10.25-10.50 GHz. The system uses the ELTA model EL/M 2112 radar, and might be used by the Department of Homeland Security. Testing will take place around the perimeter of Lake Moultrie in South Carolina.
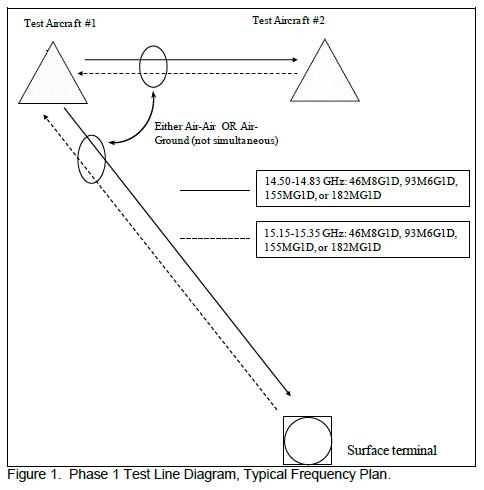
- L-3 Communications filed an application and exhibit for special temporary authority to test a prototype high-capacity airborne networking system. The data links will be between a ground station and an aircraft, and between two aircraft. Operation will be in the vicinity of Monterey, California on 14.50-14.83 GHz and 15.15-15.35 GHz. “The RF transmissions will utilize root raised-cosine (RRC) shaped offset QPSK modulation, at various symbol rates, with shaping factor (alpha) of 0.33. All transmitted data will be encoded with a rate-7/8 turbo product code prior to transmission.” “All transmissions will use identical 9.5” parabolic dish antennas.”
- Raytheon Network Centric Systems filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to “develop and demonstrate a mobile surveillance system based on commercial-off-the-shelf radar (SR Hawk Radar SRC-2362) and electro-optical/infrared cameras to monitor international borders.” Operation will be near McKinney, Texas on 16.21-16.50 GHz.
- Raytheon Network Centric Systems filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to “develop and demonstrate a mobile surveillance system based on commercial-off-the-shelf radar (DRS Manportable Surveillance and Target Acquisition Radar (MSTAR)) and electro-optical/infrared cameras to monitor international borders.” Operation will be near Las Cruces, New Mexico on 16.75-17.25 GHz.
- Samsung filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to “[f]ully characterize the radio channel at mmWave frequencies for mobile, outdoor environments to understand path loss, angular spread, delay spread, NLOS beamforming and blocking issues.” “This will help design mmWave communication systems, providing multi-Gbps data rates for wireless mobile services within new spectrum bandwidth and therefore meeting the challenges raised by the on-going mobile data explosion.” Operation will be on 27.925 GHz in Richardson, Texas.
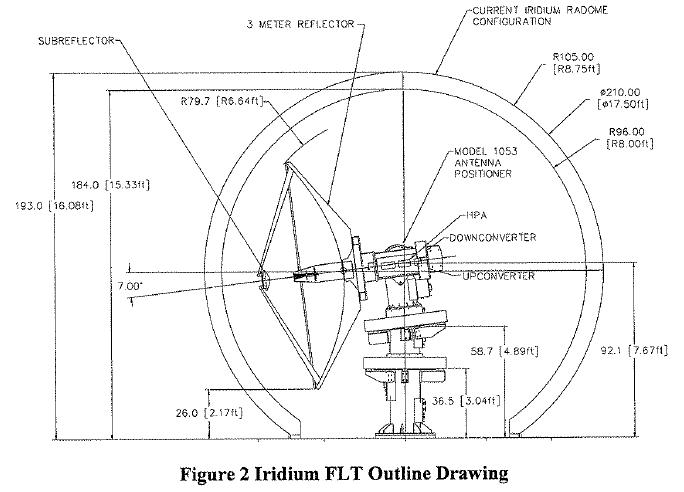
- L-3 Communications Datron filed an application with exhibits for experimental license to conduct testing of Iridium satellite system feeder-link-terminals (FLTs) related to retrofit work.” The applicant “will retrofit the current 27 FLTs to address obsolescence and maintenance issues as well as modernizing hardware and software interfaces. As many as 12 new FLTs will also be built in the future to support the latest generation of Iridium NEXT satellites currently being planned and designed.” Operation will be in Simi Valley, California on 29.1-29.3 GHz.
- Google filed an application for special temporary authority to conduct “experiments using test vehicles equipped with automatic cruise control radars in a manner that extends the sensing range of the radars when a vehicle is not in motion.” “Each Google test vehicle contains several off-the-shelf automatic cruise control (ACC) radars certified for use in the 76.0-77.0 GHz band.” “Several ACC radars will be mounted on test vehicles and the vehicles will be driven through a variety of traffic situations, including along freeways and urban surface streets and through complex intersections. The radars will operate at a radiated power of 60 uW/cm2 at 3 m (i.e., the current in-motion criterion) both while the vehicles are in motion and stationary. Because the power will not exceed the current in-motion criterion, Google believes the experiments will not increase the likelihood of harmful interference to any user.” Operation will be in the San Francisco Bay area. (The FCC has separate in-motion and not-in-motion emission limits for these vehicle radars to prevent prolonged human exposure to RF energy while the vehicle is stopped. I thus find it odd that Google links the in-motion criterion to “interference.”)
- Sierra Nevada Corporation filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to conduct ground testing of an Autonomous Landing Guidance (ALG) radar system. This is intended to allow “a fixed wing aircraft pilot to safely execute takeoff, approach, and landing maneuvers in low visibility conditions such as that caused by thick fog or blowing sand and dust.” “The ALG system is a derivative of other Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC) products currently in evaluation programs that provide similar landing situational awareness for rotor wing aircraft pilots. ALG is a millimeter wave (MMW) frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) radar with a narrow 1.0 beamwidth that is scanned over a 25° by 10° field of regard twice per second. During the scan the radar return data is processed by computer to extract the amplitude and the range to the ground. The computer accumulates all of the range and amplitude data over the field of regard and displays a three-dimensional representation of the ground to the pilot on a flight deck display.” This ground testing is a prelude to flight testing, at which time Sierra Nevada will apply to modify its experimental license. Operation will be at several California and Nevada locations on 94 GHz.