This summarizes a selection from 215 applications for the Experimental Radio Service received by the FCC during October, November, and December 2011. These are related to AM broadcasting, FM broadcasting, spread spectrum on HF and VHF, unmanned aerial vehicle control, electronic warfare support, small satellites, white space technology, video production, managed access, TV interference, RFID, and radar. The descriptions are listed in order of the lowest frequency found in the application.
Archive for the ‘WiMAX’ Category
Experimental Radio Applications at the FCC
Sunday, February 5th, 2012Experimental Radio Applications at the FCC
Sunday, November 6th, 2011This summarizes a selection from 173 applications for the Experimental Radio Service received by the FCC during August and September 2011. These are related to long-range low-frequency radar, amateur radio, shortwave data, wireless microphones, single-sideband, mine detection, millimeter-wave communications, signal intelligence, automotive radar, satellite feeder links, meteor-burst communications, aircraft telemetry, white space systems, border security radar, 3G and 4G applications, RFID, wind turbine testing, unmanned aerial vehicles, spacecraft telemetry and control, aircraft passenger broadband, and autonomous aircraft landing systems. The descriptions are sorted by the lowest frequency found in the application.
ITU Loosens Hold on Term “4G” – Now Calls it “Undefined”
Thursday, December 9th, 2010The debate won’t end but the volume is dropping on the what-is-4G controversy. Previously, I’ve written about the ITU’s characterization of 4G as only applying to the two radio technologies it has designated as IMT-Advanced: LTE-Advanced and WirelessMAN-Advanced (the latest version of WiMAX).
Experimental Radio Applications at the FCC
Saturday, August 14th, 2010This summarizes a selection of applications for the Experimental Radio Service received by the FCC during July 2010. These are related to high-frequency data, military communications, environmental data collection, synthetic aperture radar, WiMAX, sensor networks, interference-resistant communications, LTE, rail transportation, air traffic control, white space networks, and RFID.
- Harris filed an application (with supporting exhibits) for experimental license to operate on various frequencies between 3 and 15 MHz to test an experimental high-frequency wideband waveform that is intended to operate at either 12 kHz bandwidth or 24 kHz bandwidth to allow faster data transfer via high-frequency communications.
- Harris also filed an application (with supporting exhibit) for experimental license to operate on 4.94-4.99 GHz in support of development of US Army’s Warfighter Information Network: Tactical (WIN-T) and Future Combat Systems (FCS) programs. Equipment is to consist of the HNRe2 Highband Network Radio, manufactured by Harris. Harris says the HNRe2 is comprised of four elements: 1) the Baseband Processing Unit, 2) the Highband RF Unit (HRFU), 3) an Inertial Navigation Unit (INU), and a GPS device. The HRFU further consists of an upconverter, a High-Powered Amplifier (HPA), a Switched Beam Antenna (SBA), a Low-Noise Amplifier (LNA), and a downconverter). The test network will consist of five fixed nodes and one mobile node. The FCC has asked Harris to justify extended testing in a band that is primarily allocated for non-government public safety use.
- Canon U.S.A. filed an application (with supporting exhibits) for special temporary authority to operate wireless devices in support of a private technology and product exhibition from September 1, 2010 through September 3, 2010 at the Jacob K. Javits Convention Center in New York, NY. Canon is planning to import many wireless devices from Japan to be used with displays during the exhibition. These devices are not FCC compliant and not expected to be FCC compliant until after the exhibition. Frequencies requested include 315.0-315.7 MHz, 2.40-2.50 GHz, 5.18-5.67 GHz, and 61.6-62.5 GHz. This application was granted on August 11.
Experimental Radio Applications at the FCC
Sunday, July 4th, 2010This summarizes a selection of applications for the Experimental Radio Service received by the FCC during June 2010. These are related to aircraft systems, WiMAX, sports telecast support, public safety communications, tactical cellular service, medical telemetry, satellite, antennas, radar, white-space devices, weapons telemetry, spacecraft communications, and broadcasting.
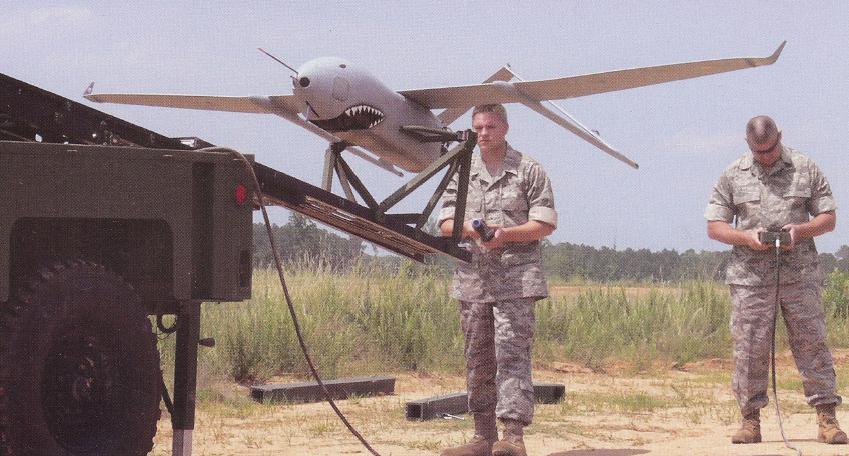
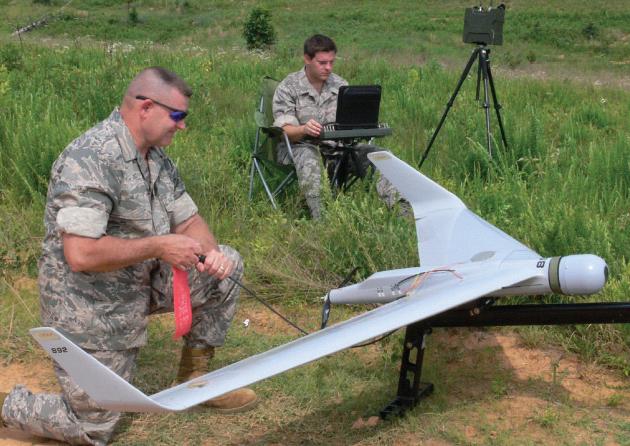
- AAI/Textron Systems Corporation filed an application (with supporting exhibits) for experimental license. The company wants to test its Shadow 200, Aerosonde, Orbiter and other unmanned aircraft systems. This is related to work for the United States Marine Corp. Operation is to be on 310-390 MHz, 902-928 MHz, 1090 MHz, 1350-1390 MHz, 1700-1859 MHz, and 4400-4999 MHz. Transmitting equipment is manufactured by Microhard Systems Corporation, Free Wave Technologies, Advanced Microwave Products, Global Microwave Systems, and Microair Avionics.
FCC staff has asked for several items of information before approving the application. The FAA operates in the frequency bands 328.6-335.4 MHz, 1090 MHz, and 1215-1390 MHz; FCC staff asks for coordination of these bands with the FAA Regional Office. In addition, the frequency bands 225-328.6 MHz and 335.4-399.9 MHz are used for military purposes, and the applicant was asked to coordinate with NTIA’s Interdepartment Radio Advisory Committee (IRAC).
- AAI/Textron Systems Corporation also filed an application (with supporting exhibits) for special temporary authority to operate on 420-450 MHz and 2000-2400 MHz for a government project apparently involving the Orbiter miniature unmanned aircraft system. There is not much information about the proposed operation, and FCC staff has asked for more details.
In correspondence to the applicant, FCC staff notes that the “Aerospace & Flight Test Radio Coordinating Council (AFTRCC) oversees the frequency bands; 1435-1525 MHz, 2310-2320 MHz, and 2345-2390 MHz. These frequency bands need to be removed or need to be prior coordinated.”
- Sportvision filed an application (with supporting exhibits) for special temporary authority for testing of an automobile race track wireless data system that is to provide data communications between vehicles in a race track and one or more fixed base stations installed along a track. Operation is to be on 2395-2400 MHz.
One application seen for this system is video image enhancement for television broadcasting of automobile racing events. The would allow television viewers to see, displayed on screen, the real-time location of cars during a racing event.
The vehicles would be equipped with GPS receivers and other sensors that generate a data packet every 200 milliseconds. The wireless system would collect those packets and deliver them to a control station in real time. “The radio itself is a direct sequence spread spectrum unit, using production radios for 2.4 GHz. The system may ultimately be deployed on an unlicensed basis in the 2.4 GHz band or elsewhere, but the high noise levels in that band in the test locations (commercial automobile race tracks) are unsuitable for development and testing of the product.”
“An Intersil baseband processor performs the Direct Sequence modulation and demodulation. It is part of a five-chipset developed for the 802.11b standard. It uses 1/4th of the standard 802.11 speed resulting in a narrow occupied RF bandwidth.”
The frequency band requested is allocated on a primary basis to the Amateur Radio Service, and coordination is to be performed with the ARRL. This application was granted on June 4.
Experimental Radio Applications at the FCC
Tuesday, April 20th, 2010This summarizes a selection of applications for the Experimental Radio Service received by the FCC during March 31 – April 15, 2010. These are related to WiMAX, unmanned aerial vehicles, radar, cellular networking, rural broadband, ultra-wideband, satellite, software defined radio, white space, adaptive networks, and amplitude companded side band.
- Clearwire filed an application for special temporary authority (with supporting exhibits) to test WiMAX equipment at various locations in California on 2502-2568 MHz. The purpose of the test is to validate the ability of equipment to operate satisfactorily in the presence of collocated equipment licensed to Sprint in the 800 and 1900 MHz bands.
- DataSoft Corporation filed an application (with supporting exhibit) for experimental license. The company says it is developing a Software Defined Radio platform featuring a configurable 400 MHz to 4000 MHz transceiver intended for markets requiring an adaptable, programmable, or cognitive radio such as TV white space, smart grid, and home networking. The experimental license is to support testing of the transceiver in a TV white space application. Due to lack of available white-space client devices, the applicant proposes using re-banded Wi-Fi equipment in the experiment. Operation is to be in Scottsdale, Arizona on 500-540 MHz.
- BAE Systems filed an application (with supporting exhibit) for experimental license to test a wireless link for use by the US Army between a soldier’s night weapon sight and night vision goggles. The wireless link will utilize WiMedia MB-OFDM Ultra-wideband technology. Operation is to be on 3.168-4.752 GHz.
- Honeywell filed an application (with supporting exhibits) for experimental license to test integration of a direct digital radio link into small unmanned aerial vehicles. This is in support of two US Army programs and one US Navy program. The radio is manufactured by AeroVironment, Inc. Both command and control, as well as video downlink, utilize the same radio. Frequency bands requested are 1711.5-1721.5 MHz and 1755-1848 MHz. Operation will be in Albuquerque and Rio Rancho, New Mexico.
- Texas Tech University Wind Science and Engineering Research Center filed an application (with supporting exhibit) for special temporary authority to operate a Ka-band mobile radar systems in support of tornado research. Operation is to be at 34.86 GHz.
- Kestrel Signal Processing filed an application for special temporary authority to allow “testing of a novel cellular network technology that is compatible with standard GSM cellular handsets.” The operation will be on the grounds of, and overlap in time with, the Burning Man event held near Gerlach, Nevada Aug. 30 – Sept. 6, 2010. Operation will be on 869-894 MHz and 1930-1945 MHz.
- CenturyTel Broadband Wireless filed an application for special temporary authority to assess the performance of equipment manufactured by IPWireless (but not yet FCC type accepted) for providing 700 MHz rural broadband service. Operation is to be at Monroe, Louisiana on 736-746 MHz.
- Inmarsat Hawaii filed an application (with supporting exhibit) for special temporary authority to initiate a program of experimentation designed to facilitate the introduction of a new Broadband Global Area Network (BGAN) user terminal type. The testing would attempt to gain knowledge with respect to link quality and to validate Inmarsat’s theoretical approach. Testing also would evaluate the interaction of the new terminal type with Inmarsat’s ground infrastructure. Inmarsat proposes to test the terminal type in the 1626.5- 1660.5 MHz transmit band and 1525.0-1559.0 MHz receive band.
- Cobham Defense Electronic Systems filed an application (with supporting exhibit) for experimental license to operate in Lowell, Massachusetts on various frequencies between 902 and 5925 MHz. Apparently, this is to be experimentation in support of the DARPA program Wireless Network after Next (WNaN). As the exhibit explains, the WNaN “program goal is to develop and demonstrate technologies and system concepts enabling densely deployed networks in which distributed and adaptive network operations compensate for limitations of the physical layer of the low-cost wireless nodes that comprise these networks. WNaN networks will manage node configurations and the topology of the network to reduce the demands on the physical and link layers of the nodes. The technology created by the WNaN effort will provide reliable and highly- available battlefield communications at low system cost.”
- Radio Design Group filed an application (with supporting exhibit) for experimental license to test a wireless intercom system that will utilize an Amplitude Companded Side Band (ACSB) RF platform. The applicant expects this to provide a stable and robust signal that is efficient in terms of transmission bandwidth and power. The applicant also expects this system to allow for an occupied bandwidth of 15 kHz per audio path including guard band. The system will be tested on 174-216 MHz and 470-512 MHz in the vicinity of Grants Pass, Oregon.
Experimental Radio Applications at the FCC
Monday, March 22nd, 2010This summarizes a selection of applications for the Experimental Radio Service received by the FCC during February 27 – March 14. These are related to smart grid, antennas, radar, military, satellite, data links, roaming services, maritime communications, WiMAX, network protocols, and UAVs.
- Sensus Spectrum filed an application (with supporting exhibit) for special temporary authority to test European Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) equipment on 412-424 MHz.
- The University of Colorado filed an application (with supporting exhibit) for special temporary authority to test the feasibility of synthetic aperture radar in an end-fire configuration. This configuration will output short (50ns) bursts of approximately 10W at 500-530 MHz in order to construct an image of objects in an adjacent parking lot. This is an attempt to prove the feasibility of a new radar configuration for a proposal to NASA.
- Oceanit filed an application for special temporary authority for a Ku-band SATCOM transmission test with an experimental ground-based phased-array antenna. Operation is to be on 13.75-14.50 GHz.
- Northrop Grumman filed an application (with supporting exhibit) for special temporary authority to test an electronically-scanned-array radar system intended to act as part of a missile interceptor system to protect against rocket, artillery and mortar threats. Operation is to be on 16.2-17.3 GHz.
Experimental Radio Applications at the FCC
Monday, March 1st, 2010This summarizes a selection of applications for the Experimental Radio Service received by the FCC during February 21-26: radar, WiMAX, MVDDS, aeronautical communications, private mobile data, millimeter wave, high-frequency data, space communications, and radiolocation.
- The Maryland Department of the Environment filed an application (with supporting exhibits) to operate a wind-profiling radar on 915 MHz. The equipment was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and fabricated by Radian International. The antenna is to consist of one steerable four-panel micro-patch phased array.
- DTV Norwich filed an application (with supporting exhibit) for special temporary authority to conduct propagation tests prior to potential full-scale deployment of Multichannel Video and Data Distribution Service (“MVDDS”) at 12.2 to 12.7 GHz in the Miami area. This is to determine the suitability of potential transmitter sites for full-scale operation, for which DTV Norwich has a license.
Experimental Radio Applications at the FCC
Sunday, February 21st, 2010This summarizes a selection of applications for the Experimental Radio Service received by the FCC during February 13-20: landslide monitoring, WiMAX, earth-station antennas, radar, military mobile data, automatic aircraft landing, psyops transmission.
- Skyport Global Communications filed an application (with supporting exhibits) to test a 55cm slot-array X-band antenna manufactured by EMS Technologies on 8218-8400 MHz. The test will be done using a satellite link between the 55cm antenna in Atlanta, Georgia and a hub in Houston, Texas using the XTAR LANT X-band satellite.
Experimental Radio Applications at the FCC
Tuesday, January 26th, 2010This summarizes a selection of applications for Experimental Radio license, and for Special Temporary Authority, received by the FCC during January 14-20: VSAT for Haiti, helicopter surveillance in Chicago, WiMAX, wideband at high frequencies, avionics, cell phone jamming, and radar.
(more…)
University of Massachusetts applies to use WiMAX with virtual network lab
Sunday, December 27th, 2009The University of Massachusetts has filed an application and supporting exhibit with the FCC for an experimental license to use WiMAX as part of the Global Environment for Network Innovations (GENI) project.
Operation will be at 2590-2600 MHz and use NEC’s WiMAX base-station hardware supporting a maximum of three sectors, a coverage radius of 3-5 km, and peak data rates of 15-30 Mbps. The base station uses an external PC controller that interfaces the base station to other parts of the GENI infrastructure.
GENI plans to support experimentation on shared heterogeneous infrastucture with programmability throughout the network, including wireless aspects. It is intended to promote innovations in network science, security, technologies, services, and applications. At this time, GENI plans to use WiMAX at 8 universities. Some sites will also use the OpenFlow standard, which allows researchers to run experimental protocols on production networks.
ADC applies to test WiMAX in Colorado
Wednesday, December 23rd, 2009ADC Telecommunications has filed an application and supporting exhibit with the FCC requesting Special Temporary Authority to test a WiMAX (802.16e) pico base station in the 2.5 GHz range. Tested will be coverage, uplink communication, and throughput in the Greely, Colorado area. Testing is in conjunction with WiMAX operator Open Range Communications. ADC partnered with WiNetworks to design the base station.